Welcome to UVM Blogs. This is your first post. Edit or delete it, then start blogging!

Archives
Categories
- discussion (13)
- exams (3)
- home (4)
- readings (5)
- resources (4)
- sidebar (1)
- syllabus (1)
- Uncategorized (1)
Site Meta
English 131: Reading the Bible
June 23 – Apocalypse(s)
Posted: June 22nd, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby

How is the account Lawrence Wright provides in “Letter from Jerusalem: Forcing the End” (e-reserve reading) related to Crossan’s argument in his chapter “The Jordan is Not Just Water” (chapter 2 of his book) and to Fredriksen’s argument in the e-reserve reading you did from Jesus of Nazareth, King of the Jews?
June 22 – Paul and the Early Christian Community
Posted: June 18th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby

Do ALL:
1. The event Christians call “Pentecost” is described in Acts of the Apostles, ch. 2; the word literally means “count to 50” (so a feast marking 50 days). In Judaism (Leviticus 23:15-21 and elsewhere) this harvest festival takes place fifty days after the Passover, which makes it, in a sense, a feast of gratitude for what took place seven weeks (or so) after Passover: God’s revelation to Moses at Mt. Sinai. So if the crucifixion of Jesus (and subsequent resurrection) took place around Passover (all four Gospels take this position), then what is described in Acts 2 is symbolically linked to (extending, revising, replacing) what happened in the Book of Exodus (the revelation at Sinai and all that entails). In what sense then do you think the Jewish-Christian Pentecost is working in relation to the Jewish Pentecost?
2. In his Acts of the Apostles, Luke tells the story of Paul’s “conversion” on three different occasions (Acts 9:3-4, 22:6-7, 26:13-14 … which makes you wonder why Luke wants to tell it three times). Crossan (p. 167) says that this experience is a trance of some kind (“there can be no doubt that Paul’s own experience involved trance–that altered state of consciousness” and then he says that Luke’s accounts “all agree on its dissociative character”). Crossan seems to be forgetting his own methodological rule that stories written about events are often very different from the original events. Paul himself gives three very different sorts of accounts and only the second (which doesn’t explicitly link to the conversion experience) has anything like a trance. So read the following from Paul’s letters: 1 Corinthians 15:1-10; 2 Corinthians 12:1-10; Galatians 1:11-17. When Paul says that Jesus “appeared” to him (1 Corinthians … and a better translation would be Jesus “was revealed to” Paul) or that “God … was pleased to reveal his Son to” Paul … Galatians), do you think we are to understand these as “altered states of consciousness” or is Paul saying something different from Luke? At a minimum, address how what Paul actually says is like or unlike what Luke presents.
3. Looking at the first 7 chapters of Acts of the Apostles, discuss your understanding of the “imagined community” that came into being after Jesus’ death? Is this like or unlike what Crossan is describing as what Jesus called the “kingdom of God”?
June 18 – Crucifixion and Resurrection
Posted: June 16th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby
Do 1 OR 2; and then do 3 OR 4:
1. Looking at the accounts of Jesus’ arrest in just Mark and John (obviously, you should feel free to consider Luke and Matthew as well, but you don’t have to address their versions in your writing), discuss how the very different portraits of Jesus that Mark and John provide for Jesus during the scene of the arrest (and you should include in this the time of prayer just before the arrest), explain how those portraits are carried through into the scene of the crucifixion itself (you might note, for example, what Mark’s Jesus or John’s Jesus say while he is dying on the cross).
2. What does it mean to say that the Gospel writers “searched the scriptures” for the account of Jesus’ crucifixion (see Crossan pp. 143-52).
3. Although Crossan himself doesn’t appear to believe in the historical reality of Jesus’ resurrection, he’s more than willing to admit that some (though not all) early followers of Jesus understood “what happened” in terms of resurrection as a bodily fact. That said, Crossan is at pains to show that, whatever the Gospel writers believed about resurrection, the accounts themselves are about something else. What is Crossan’s point about this and what is his evidence?
4. “How many years was Easter Sunday?” That’s the title of the chapter 7 of Crossan’s book. What is the point of that question and how does the chapter attempt to answer it?
A Christian type-scene? Exploring John’s Gospel
Posted: June 15th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby

Christian Adaptation of Hebrew Narrative: reading the pericope of the meeting between Jesus and the Samaritan woman (John 4: 5ff.)
It is instructive to consider the cultural context of John’s Gospel, especially in light of subsequent history. In 90-100 C.E. the Jewish Christian community—the Jesus movement—was struggling as a marginalized sect within Judaism as a whole. As John Dominic Crossan suggests, it was “losing” the battle with the Pharisees over precisely which group would lead Judaism in the post-Temple world (a world in which the spiritual life was no longer defined in terms of the priesthood that presided over Temple sacrifice, central to Jewish spirituality since the earliest days). Today, the world Christian population may be 1 billion, while the world Jewish population is probably barely over 10 million, 1% of the Christian population. Clearly, in purely historical terms, Jesus’ “mustard seed” parable has come to pass: from a little seed something has grown of enormous proportions. Christianity has always been a faith that has sought converts, and once it became clear that there were no more converts from Judaism itself, it turned its sights on the pagan Greco-Roman world, a world that, as the historian Peter Brown has shown, hungered for a deeper spiritual life. Judaism has never been a proselytizing (i.e. “converting”) religion; and that fact, along with a history of violence against Jews, helps explain its relatively small population.
But the cultural marginalization of that early Christian community also tells us something of why John writes what he does: he believes he must convince his fellow Jews (or whoever will listen) that Jesus, and Jesus alone, is the Messiah: there is no future human king (military leader) coming to liberate the people from Roman rule. But the very fact that he knows his group is losing leads John to demonize his fellow (non-Christian) Jews as children of the devil. In later history, that “invective” will be used to promote active persecution of Jewish populations by Christians who within a few centuries will dominate what is left of the Roman Empire (and that persecution will continue down into our own day, though you can’t blame it all on Christianity, and you certainly can’t blame it all on John, who of course was himself Jewish).
That is the cultural context of John’s Gospel. And it affects both the content of his writing—his insistence that faith in Jesus as the Messiah is what really matters in our quest for “eternal life”—and his way of telling the “Jesus story”(his style or rhetoric; that is, “how” he goes about saying what he wants to say). We will examine the issue of Jesus’ identity a bit more as we go along, but John’s basic mission as a writer helps explain much of his gospel, including the story of the Samaritan woman at the well. John wants to use the symbolic vocabulary of Judaism itself to radically redefine its central spiritual vision: how the people relate to God and how this is linked to the promised Messiah as the restorer of the covenant between God and his people.
John uses the betrothal “type-scene” to effect this transformation of Jewish thought from “within.” The introduction to his version of this oft-repeated scene—man meets woman at the well—comes in 4:1-6, where the recollection of Joseph’s burial place (cf. Joshua 24:32) is itself symbolic, a marker of sorts that what is to follow (the “type-scene”) must be considered very carefully; this is so because the earlier passage from Joshua was meant in its original context to mark the Israelites’ entrance into the promised land as a sort of “planting of a seed” of past promises and past triumphs: The burial of Joseph’s bones serves as an emblem of the possibility of sustaining God’s blessing and presence even in the midst of hardship. John’s recollection of this scene of planting the past to create a better future is his way of marking the necessity of remembering: to remember the past is critical to the future, to the possibility of fulfilling the terms of the covenant. Memory, as we know from our earlier work this term, is critical to the cultural survival of a people (without a sense of a shared past people cannot sustain a common identity), but in biblical thought, remembering always also means revising our memory to understand more (to create the possibility of a new future precisely as the fulfillment of past promises … this is what the covenant is all about). So John is suggesting that the type-scene that follows will be linked somehow to his effort at once to remember the covenant and to revise it, to redefine its meaning as we move toward the future (what John in ch. 4 calls the approaching “harvest” or final fulfillment of the covenant). If the scene at the well is what must be remembered and revised, the introduction, in short, is meant to call our attention to the necessity of remembering and revising (the only way to move into the future).
So what is the type-scene all about? How does it at once remember the past and revise it? What we see are, first, the details that John borrows from the type-scene itself (the conventions of the scene from past examples) and, second, the beginnings of the process of John’s re-application of the scene’s accepted meaning in the new context of Jesus’ life and teaching: his status as the promised Messiah. The details include:
1. Jesus’ journey to or through a “foreign land” (Samaria), and the woman reminds him that the Jews and the Samaritans are really strangers to each other’s cultures despite a common ancestry
2. in this foreign land he meets her at the side of a well ; the “girl” (not a virgin or “maiden”) draws water for him (and this act always represents a “sign” of some kind)
3. an example of how the borrowing becomes a revision: though she is not a virgin, her marital status is an issue; but Jesus’ provocation of the revelation that she is living with a man to whom she is NOT married defines her sexual status in terms of its sinfulness (so what she needs more than a husband is someone to “save” her from her sinful condition); it is worth noting here, though, that, as the scene with the adulteress in ch. 8 shows, Jesus is a merciful savior, for he does not condemn the adulteress for her sin but loves her and asks that the others show mercy to her (in John, while Jesus has incredible power and authority, he isn’t really the harsh judge and condemner that he was in Matthew’s Gospel)
4. after he shows “clairvoyant” knowledge of her life, she goes to her the people of the city to bring news to others (the “good news”: I may have seen the Messiah); this bringing of news to others is also part of the type-scene of the betrothal-at-the-well (see Genesis 24:1-61 and 29:1-14 and Exodus 2:15-22)
5. a second example of how John’s scene adopts and adapts the type-scene: we have something very different from a literal betrothal, but in the previous chapter (John 3:29-30), John refers to Jesus’ presence in the world as akin to the presence of the bridegroom, the one who will be symbolically betrothed to all people
6. the type-scene is supposed to end with an invitation to a meal: though here, we get only water at first, and then a vague reference to being hungry at 4:31-34 (Jesus is somehow offering food?) / or perhaps we need to await the completion of the scene elsewhere; in any event there are enough references to food and an invitation to stay that we understand the basic completion of the traditional type-scene: perhaps without understanding all of it, we grasp that somehow the image of an invitation to partake of food—as the culmination of the betrothal scene—is moving from literal food to figurative or spiritual food.
Before I get to some other questions about John’s use of the type-scene, we should remember this statement from Alter: “The type-scene is not merely a way of formally recognizing a particular kind of narrative moment; it is also a means of attaching that moment to a larger pattern of historical and theological meaning. If Isaac and Rebekah, as the first man and wife born into the covenant God has made with Abraham and his seed, provide certain paradigmatic traits for the future historical destiny of Israel, any association of later figures with the crucial junctures of that first story [the betrothal-scene] … will imply some connection of meaning, so further working-out of the original covenant” (Art of Biblical Narrative, p. 60). In the person of Jesus, John certainly imagines a “further working-out of the original covenant.” With that in mind, here are some questions to think about as a way of understanding John’s re-deployment or revision of the type-scene:
Question 1: what did the type-scene previously (that is, in earlier examples) symbolize in relation to the covenant and how will this tell us something about what John is asking his Jewish readers to re-imagine about itself in relation to this strange teacher / prophet?
Question 2: why is there a continuation of phrasing going from 4:14-15 to 6:32-34? How does the passage running from 6:32-59 complete the type-scene from ch. 4?
Question 3: If all this matters to John because it is Jesus’ identity that matters, who exactly is Jesus, and how does John define that identity in terms of images and themes from the Hebrew Bible? (Consider, among other things, the following: how does the opening of John’s Gospel look back to Genesis 1? And how is the claim put forth in 5:16-18 related to what Jesus says in 4:46, 6:20, and 8:58? —and consider this last passage in relation to Matthew’s genealogy at the opening of his Gospel).
June 16 – the Jesus Story (parables and miracles)
Posted: June 15th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby
Do ALL:
1. Explain Crossan’s understanding of “radical egalitarianism” and “open commensality” as manifestations of the Kingdom of God.
2. Explain Crossan’s distinction between healing and curing an illness / disease.
3. Do either A or B:
A. Look at Crossan’s discussion of the exorcism of the Gerasene demoniac (pp. 88-91). Tell me how you understand the implications for understanding how the text of the Bible is a written thing, that is, a way of representing experience rather than a “literal” account of what really happened. (There are a variety of ways of responding.)
B. Read “Back from the Dead” (Crossan pp. 93-95) and read chapter 11 of the Gospel of John. Is there a way of understanding the raising of Lazarus story as anything other than literal (that is, that Lazarus was brought back to life)? (We’ll deal with the issue of “resurrection” on Thursday.)
June 15 – beginning the New Testament
Posted: June 12th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby
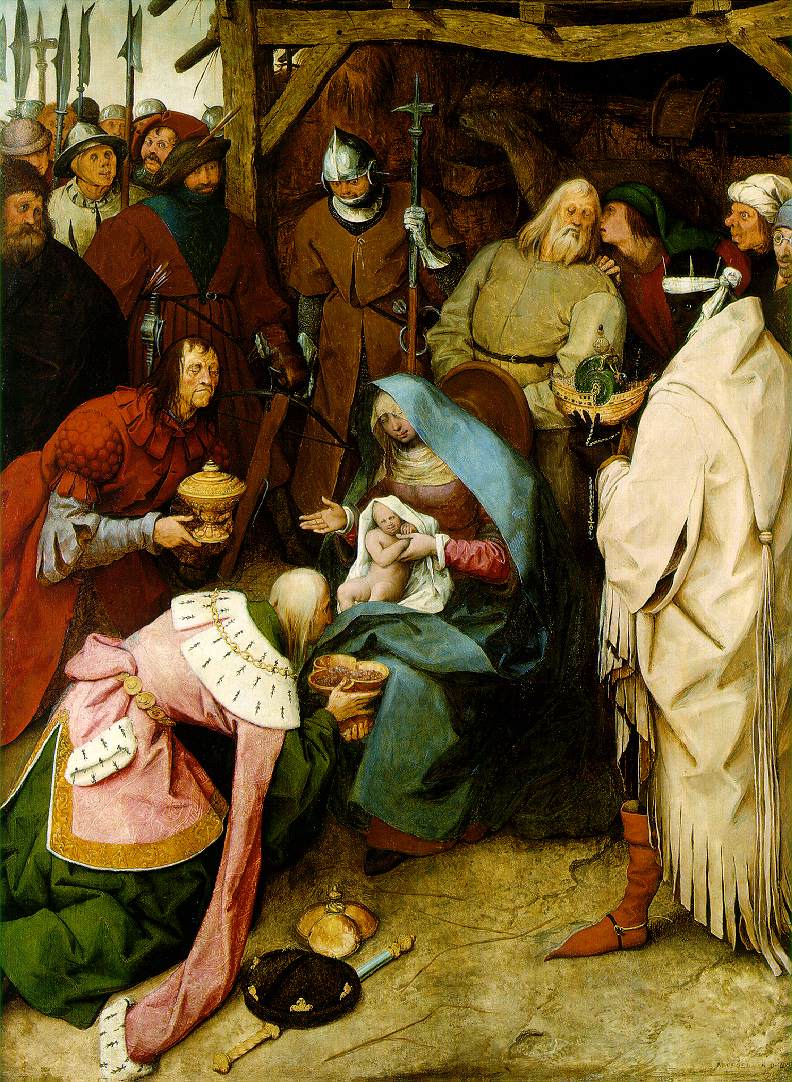

Do ALL (but you don’t have to go into great detail on each response):
1. How is Luke using a type scene?
2. How are Matthew and Luke using the early life of Jesus (whether this is fictionalized or not) to imagine or reimagine the Jewish notion of the Messiah?
3. Make a quick list of how Luke and Matthew’s Nativity stories are different.
4. To the extent that Jewish apocalypticism swirls around the person of Jesus, how do you understand Crossan’s perspective on this as recounted in chapter 2, “The Jordan is not just water”?
June 11 – Ruth
Posted: June 9th, 2009 by Andrew Thomas Barnaby

Do ONE:
1. The text from Ezra (9-10:15) includes the ban on marriage to foreign wives. How is that ban in dialogue with the Book of Ruth? (You might want to think about this in relation to Alter’s argument about the “type-scene,” Art of Biblical Narrative, ch. 3.)
2. Here’s a question from June 1st (and hopefully you’ve learned that revision–to see again–is at the heart of the experience of reading the bible): “In a Jewish Bible, Ruth does not provide a buffer between Judges and Samuel. What is the composite effect that arises from moving directly from Judges into the first story in 1 Samuel. How do you understand this relationship?” That was the question Lisa wrote. Now consider this a different way: in later editions of the Bible (that is, NOT the Hebrew Bible), Ruth was moved from the Writings (Kethuvim) to what we might call the historical sections, and it was put between Judges and 1 Samuel. As you think about the end of Judges (the story of the Levite’s Concubine) and the beginning of 1 Samuel (the type scene with Hannah that leads to the birth of Samuel), can you imagine any purpose served by connecting Judges to 1 Samuel by way of Ruth?
