This post was written by Bavin Balakrishnan ’20. Connect with him on LinkedIn.
It is common knowledge that carbon emissions is a major contributor to the climate impact crisis. It is even more common to hear about the reduction of carbon emissions to mitigate the impact.

What about the carbon already in the atmosphere? A common solution to develop carbon sinks is to plant trees, which is a great start to replace the deforested area. However, as the population grows and more land is converted into cities, we need to re-assess the previously suggested solution.
During our first semester in the SI-MBA program we were introduced to the following equation regarding human impact to frame what factors affect this developed by Commoner, Ehrlich, Holdren[1]:
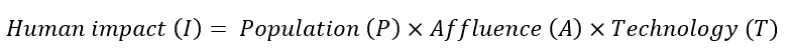
As established earlier, the population is expected to continue rising with estimates of world population reaching 8.5 billion by 2030.[2] Similarly, affluence (or consumption) of people will continue to increase as developing countries are increasing their GDPs, which is commonly used as a proxy to judge consumption. Finally, technology represents the resources required to produce the units of consumption, thus increases with affluence.
So, what’s the solution? Simple algebra can reframe this equation to our benefit and reduce the human impact:
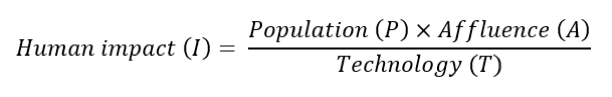
This equation represents that using our resources efficiently can significantly deter our impact. A resource that we are currently failing to make more efficient is the soil. Carbon naturally belongs in the ground and is the prime factor that creates an efficient ecosystem within the soil.

The image identifies fundamental concepts behind regenerative agriculture, however, these holistic practices are not currently applied by majority of farmers as they believe it is not financially feasible. A common misconception in the farming community, especially within developing countries, is that monoculture farming will generating the highest revenues. Though this may have been true in the early days, with strong soil health and support from large enterprises such as Monsanto, those practices have depleted the soil of its natural benefits.[3]
Contrary to the misconception, those farmers who implemented regenerative agriculture practices have rejuvenated their land, which paid dividends through higher crop yields and greater soil health for future generations.
A caveat in this solution, it needs to be applied at a local level. On the other hand, the food industry is a globalized market with customer demands for exotic foods continuously increasing.[4] In order to deal with this supply short, the solution is glocalize the food supply chain, which refers to the production of native crops at a local level to meet the demands of global scale. This requires co-ordination between farmers so that an individual doesn’t face the burden / risks associated with monoculture production.
This is my case to create
a platform for farmers in their respective countries to the power of
agriculture back in their hands and regenerate their land, reduce the human
impact, and provide hope for future generations.
[1] https://jpopsus.org/full_articles/holdren-vol2-no2/
[2] https://www.un.org/sustainabledevelopment/blog/2015/07/un-projects-world-population-to-reach-8-5-billion-by-2030-driven-by-growth-in-developing-countries/
[3] https://www.globalresearch.ca/the-seeds-of-suicide-how-monsanto-destroys-farming/5329947
