Vermonters made a total of 3,533 scam reports to the Attorney General’s Consumer Assistance Program (CAP) in 2024. Leading the list was the “Computer Tech Support” scam, totaling almost 30% of the top scams reported. This scam tricks people with sudden alerts about alleged computer issues, such as expiring antivirus software or malware infections. Variations also include fake messages to the consumer’s phone or email about packages or unauthorized orders. Noticeably, this marks the fourth consecutive year this scam has ranked as the most reported.
The email extortion scam has returned to the list after a four-year hiatus. These troubling emails threaten to release personally compromising photos and information. A new and disturbing twist on this scam is the emails include screen-captured images of the recipient’s home from online map services to further unsettle recipients and pressure them into complying with the scammers’ demands.
“Educating consumers is the best way to protect Vermonters from scams,” said Attorney General Clark. “With most scams originating overseas, they are incredibly difficult to shut down. These are the top scams to look out for.”
More information about scam prevention strategies and other resources can be found on the CAP Connection blog, at Attorney General Clark’s social media sites, and by signing up for VT Scam Alert System scam alerts. To sign up, visit CAP’s scam prevention website. Roughly 9,000 Vermonters have signed up to receive alerts.
The VT Scam Alert System was previously established through a partnership with Vermont Emergency Management that granted the Attorney General’s Office permission to manage a contact list and issue alerts utilizing limited features of the Vermont Alert system. VT-ALERT is the state’s notification system for emergencies, severe weather, roadway interruptions and hazards, environmental hazards, and more. This year, the Attorney General’s Office and VT-ALERT are strengthening this partnership by merging the existing VT Scam Alert System with the well-established VT-ALERT system.
“Vermonters have long relied on Vermont Alert to notify them of floods, hazardous travel, local boil water notices, and countless other issues that impact their lives,” Vermont Emergency Management Director Eric Forand said. “Scam alerts will add a layer of protection of Vermonters’ financial security for those who choose to receive them.” Attorney General Clark thanked Vermont Emergency Management for their partnership.
In the future, whenever someone signs up for VT-ALERT, they will have the option to choose to receive notifications about scams among the list of options. VT-ALERT’s 72,000 existing users can also update their preferences to add scam alerts.
Attorney General Clark reminds Vermonters to report scams and get support if you or a loved one falls victim to a scam by contacting her Consumer Assistance Program. Call 800-649-2424 or email AGO.CAP@vermont.gov.
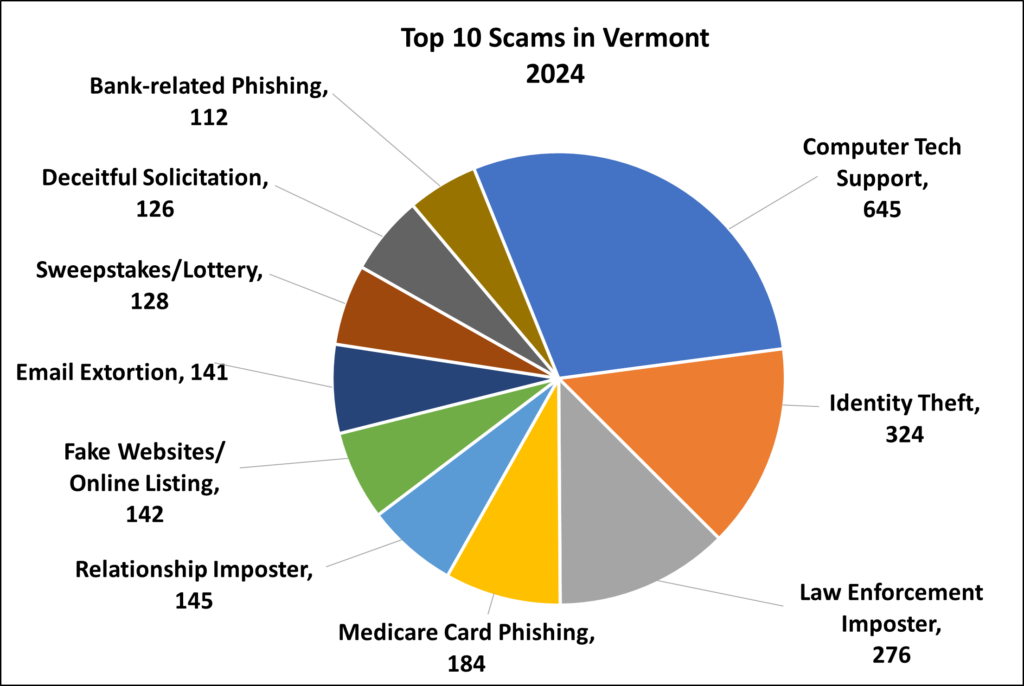
The Top 10 Scams of 2024:
| Top 10 | Scam Type | Reported Totals |
| 1 | Computer Tech Support | 645 |
| 2 | Identity Theft | 324 |
| 3 | Law Enforcement Imposter | 276 |
| 4 | Medicare Card Phishing | 184 |
| 5 | Relationship Imposter | 145 |
| 6 | Fake Websites/Online Listing | 142 |
| 7 | Email Extortion | 141 |
| 8 | Sweepstakes/Lottery | 128 |
| 9 | Deceitful Solicitation | 126 |
| 10 | Bank-related Phishing | 112 |
Total Reports in the Top 10: 2,223
Total Number of All Scams: 3,533
A chart containing the Top 10 Scams of 2024 can be found here.
A complete overview of the Top 10 Scams of 2024, including how to spot them, is available here.
Top 10 Scams of 2024 Overview
The scam: You receive a phone call, pop-up, email or text message on your computer claiming to be a well-known company; sometimes it’s a tech company like Norton, Apple, or Microsoft, or it’s Amazon saying your credit card has been charged, or there is a package delivery delay. They will urge you to contact them due to a problem: your electronic device has a virus, your device security subscription has been automatically renewed, or you have been charged for services you did not receive or request. You may be prompted to click a link or call a number to contact. They will try to persuade you to give remote access to your device to fix the problem and sometimes will even ask for immediate payment for their services or have you login to your online bank account to initiate a transfer.
How to spot the scam: Companies will not call with tech support unless you request that they contact you. Legitimate tech support companies do not display communications to their customers as random notices or alerts on your device. Tech support will not call you to warn you about security incidents, that your account has been renewed for a subscription you do not recognize and will not send you random links with instructions for you to click on URLs. If you receive a package that you do not recall ordering, check your statement history to see if you have been charged. Packages without a return address are highly suspicious.
What to do: When contacted about a supposed business relationship, take steps to verify, especially if you do not remember purchasing the products/services. Never click on links or provide remote access to your computer from an unknown sender or pop-up message on your device’s screen. If you receive a pop-up message you cannot click out of, shut down, restart, or unplug your device. If you get a call from “tech support”, hang up. Also, be careful when searching for tech support online. Some users have been scammed by calling inaccurate phone numbers listed online. If you are concerned about charges made to your accounts, log in to your account directly and contact your financial institution. If you receive a package that you did not order, write “return to sender” on it and give it back to the mail carrier.
The scam: Your personal information is compromised and may be used for another’s financial gain. This can look like: an unauthorized charge on an account, receiving a letter about a new account opening or a data breach notification. You might stop receiving legitimate bills and other mail or start to get bills for products and services that you didn’t arrange. Accounts you are not familiar with may be listed on your credit report.
How to spot the scam: Beware of communications denoting unexpected bank transactions, credit card or benefit applications. If your expected bills are not showing up, or you are receiving correspondence in someone else’s name, report it.
What to do: Don’t give out personal information, such as your Social Security number, passwords, personal identification numbers, and financial accounts. Review your credit reports at least once a year. (You can access your credit report for free). Carefully check bank account statements and benefits to verify transactions. Shred documents and expired credit cards before you throw them out. Verify security breach notification letters received on the Attorney General’s website. If your information has been stolen by an identity thief, take identity theft protection steps. You can safeguard your financial information by placing a credit freeze on your credit report.
- Law Enforcement Imposter
The scam: You receive a phone call unexpectedly, claiming to be a police officer, sheriff, U.S. Marshall, or similar. The caller will claim there is outstanding legal action. They may claim you have missed jury duty or there is a warrant for your arrest, for example. When you engage, urgent payment is demanded to make the problem go away, or you may be asked to fill out a detailed personal inquiry form. Payment does not solve the supposed problem, and they keep calling.
How to spot the scam: Law enforcers do not warn you ahead of time about a pending warrant or arrest. Legal action follows standard due process and there is a lot of paperwork, typically delivered by mail or served in person. For jury duty assignments, you first must be selected through a process called a jury draw that occurs at the courthouse.
What to do: Hang up on all arrest threats and report them. Watch out for similar government imposter scams that purport to be agents of government, including from the Social Security Administration, the IRS and more.
The scam: Scammers will call, often with a live call and from a spoofed caller ID number and pose as Medicare representatives to gain your personal information and money. These scams are most frequent during times of open enrollment but can occur year-round. The scammers will state they need your Medicare card number or Social Security number to keep your coverage active and verify medical information. The calls may also claim that coverage is expiring or in need of renewal. Scammers will also ask if you received a “new Medicare card.”
How to spot the scam: In general, Medicare cards do not expire. Unless you have called Medicare using the 800 number on the back of your card and requested a callback, Medicare will not call you. Medicare representatives will never call you in an attempt to verify your information, sell you products, tell you that your coverage is expiring, or to issue you a new card.
What to do: Never provide your Medicare number or other personal information and payment to unknown callers. In Vermont, representatives of the State Health Insurance Assistance Program (SHIP) at 1-800-642-5119 through local Area Agencies on Aging can help address Medicare questions. Other questions and concerns about Medicare coverage can be directed to Medicare at 1-800-MEDICARE.
The scam: Scammers pose to be someone you trust and pretend to be in a crisis to convince you to send them money. They may also ask you for a favor. These scammers pose as grandchildren, friends, relatives, budding romantic partners, and other close contacts. Scammers impersonate people you adore and play on your fears to have you send money urgently. After the initial contact, you may be redirected to a lawyer or parole officer. Sometimes the voices in the phone call sound like relatives due to scammers utilizing artificial intelligence. In-person couriers may also come to retrieve funds.
How to spot the scam: Contacts come in as calls, emails, or online messages. Sometimes it’s someone you haven’t heard from in a while. They require urgency and ask for secrecy. You may be instructed not to speak to your loved one on the phone. For new relationships, they have excuses as to why they can never meet in person, they won’t video chat with you when you would like, they have a pressing need for financial help (at any point in the relationship).
What to do: Take steps to verify. Check out if they really are who they say, even if they sound like a loved one. Slow down your response and contact someone you trust to verify if there is an emergency. You can also choose a “code word” with friends and family to verify the person is who they claim to be. If they don’t know the word, they are not your friend or family member. Do not give money to in-person couriers. For new online relationships, involve your inner circle as a sounding board. Use existing image search tools to find out more about the person, such as whether the profile is duplicated. Ask for candid, uncommon photos to be taken and sent in the moment and don’t trust fuzzy, or alterned pictures.
The scam: Fake websites or phony listings draw you into a purchase that is enticing. Listings may include online storefronts, Facebook Marketplace and Craigslist posts that don’t deliver after payment has been made, cheap pet sales, and websites with steep discounts. This scam can also appear in online rental listings as well as target online sellers.
How to spot the scam: Be skeptical of unrealistic offers. Watch out for requests for money in any form when not made in person. Scammers likely will not want to talk on the phone or meet in person. Heed warnings in user reviews and other online commentary.
What to do: Investigate the person/profile of the seller. If their profile is new and they have no friends and photos, they are likely a scam. Verify the website URL is the actual business’ site and not a copycat. Research new websites you are considering doing business with by looking up online reviews and business registrations, taking note of how long the company has been operating. Perform online searches of the business with “scam” and “complaints” to see if issues generate. For classified-type listings, complete your transactions in cash and preferably at a safe place in person.
The scam: You receive an email, and sometimes a text message, where the scammer attempts to manipulate you with bribes and threats. In most cases, they will threaten to expose embarrassing content about you online. They may threaten physical harm if you do not comply with their demands.
How to spot the scam: Scammers will use high-pressure tactics to create a sense of urgency, leaving you little time to think or verify the situation. They will demand payment through untraceable methods: cryptocurrency, and crypto ATMs, gift cards, and money transfers.
What to do: If you encounter a situation like this, stay calm and avoid sharing any personal information. Do not engage with the scammer at all. If the email sender is from a friend’s account, contact them by phone and let them know their account has been hacked.
The scam: You will be notified by phone, email, or mail that you won a prize or a quantity of money. In some cases, you will even receive a realistic-looking check – but it is fake! You are instructed to pay fees and give your financial and personal information to claim your prize. They often use a legitimate sweepstakes name, like Publishers Clearing House.
How to spot the scam: Legitimate sweepstakes and contest businesses, like Publishers Clearing House and Mega Millions lottery, will contact you in person if you win a major prize. For prizes under $10,000, the notification is done through certified mail by overnight delivery services (FedEx, UPS). They will not contact you by phone, nor require a payment or processing fee to release your prize.
What to do: If it sounds too good to be true, then it’s not true. You don’t need to pay fees to an entity, whether for processing, shipping/handling, insurance, and taxes, etc., or give your financial information in order to claim a prize.
- Deceitful Solicitation
The scam: You receive unsolicited communication with a deceptive promotion. Unreal offers may appear to be from well-known businesses, like Xfinity, DirecTV, or Dish Network. Solicitations may purport affiliation with a charitable cause or make low-ball offers on the sale of real estate, urging recipients to complete an enclosed one-page contract to sign over your home.
How to spot the scam: Beware of unsolicited offers you cannot verify. Be especially weary of offers that ask you to complete the transaction quickly or in one sitting.
What to do: Hang up on unknown callers and let calls go to voicemail. When you receive mailings, take extra time to review by inspecting the details and consulting your personal contacts. Never give over your payment information or sign on the line when you don’t understand the offer or details.
- Bank-related Phishing
The scam: You receive an email or phone call claiming to be from a bank or entity that keeps personal identifiable information (PII), like the Social Security Administration. The communication may claim that your account is in danger or has been suspended, or that your card is on hold due to suspicious activity. Emails may also include links to phony websites. Phone calls may claim that there has been fraudulent activity involving your account, and the scammers demand personal information about you and your account.
How to spot the scam: Scammers mask their actual identity by changing the sender’s name to the name of the cloned entity. Look at the email address before opening the email. You will often find an account not affiliated with the claimed entity. Similarly, scammers can spoof phone numbers of real businesses. If you answer a call that appears to be from a company with which you maintain an account and they ask for your personal and/or account information, hang up and call the company directly on a number you trust and verify their attempt to contact you.
What to do: Do not reply to the email or click on any links or attachments included on the message. If you receive a call, hang up the phone. Correspond with entities only using verified contact information, such as information listed on your statement.
Scams Reported by Businesses in 2024
Of the 3533 scams reported to the Consumer Assistance Program (CAP), 191 were submitted by Vermont businesses.
The 5 most common scams for businesses include: Fake orders, utility disconnection threats, imposters of business personnel, government imposters, and business identity theft.
The top scam for businesses to look out for is Order Fraud (fake orders of goods or services):
In 2024, CAP received 65 reports from Vermont small businesses experiencing fake order requests, in which scammers pose as customers initiating purchases. The purchases could be of business’ products, or of the services the business provides. In this scam, businesses are typically offered fraudulent forms of payment (fake checks, stolen credit cards). Sometimes businesses fulfill orders that are never paid for because the scammer’s check bounces, and stolen credit card charges are reversed.
Sometimes, scammers request overpayments to be sent elsewhere, such as when a scammer sends a fake check to cover the cost of a wedding service but sends too much money and asks the wedding vendor to redirect the overpayment to fake wedding vendor by peer-to-peer payment services (PayPal Friends/Family, Venmo), or wire transfer. This year, several Justices of the Peace reported fake requests for wedding officiant services. Scammers similarly targeted realtors by claiming to be property owners seeking a company to help them sell their homes or land. Scammers used actual names listed on deeds, making it difficult for realtors to verify ownership.
To reduce fraud incidents, always use multiple methods to verify the legitimacy of a potential buyer. While it may be difficult, take steps to verify. Especially for large orders, use address verification services, card verification value (CVV) checks, and multifactor authentication for consumer accounts. Do not accept overpayments. Instead, ask for the correct payment amount to be reissued. You never want to be in the position of paying expenses on the consumer’s behalf.
CAP further encourages businesses in Vermont to take the following steps to help prevent scams:
Train Your Employees: Your best defense is an informed workforce.
Verify Invoices and Payments: Check all invoices closely. Never pay unless you know the bill is for items that were actually ordered and delivered. Tell your staff to do the same.
Be Tech-Savvy: Don’t believe your caller ID. Imposters often fake caller ID information so you’ll be more likely to believe them when they claim to be a government agency or a vendor you trust.
Know Who You’re Dealing With: Never send money to parties you cannot verify. Check registration history, recommendations, and confirm contacts by calling. Before doing business with a new company, search the company’s name online with the term “scam” or “complaint.”
Businesses are encouraged to call CAP to report scams, ask questions, and get resources.
